Research Work
Detection of cardiac bio-marker using paper based microfluidic sensor
This work was also collaborated with IIt gandhinagar.Institute of Advanced Research Gandhinagar
Abstract
We have designed and developed a a paper-based microfluidic sensor through which we have sensed the antibody-antigen reaction.Paper-based devices currently are the better option for fabricating microfluidic diagnostic devices because , they are low cost, lightweight, simple to operate and non-invasive.We used a Nitro-Cellulose Membrane(NCM) as a paper substrate and using wax paper we created a hydrophobic barrier to make a hydrophilic channel through which fluid can flow.
We integrated the screen-printed electrodes with this channel using silver conductive paint for sensing the resistive signal.We measured the resistance of antigen and the resistance of antigen with the graphene-antibody conjugate reaction.We use the Fatty Acid Binding Protein(FABP) antibody and graphene quantum dot solution to make graphene-antibody conjugate.We measured resistance values of antibody-antigen reaction at different concentrations of antigen
- Date : 01.02.2018
- My Designation : Project Fellow
- Duration : 6 Months
- Institute : IAR, Gandhinagar
Supervisor- Dr. Alok Pandya
"Department of Biotechnology and Bioengineering "Microfluidic deals with the behavior that apply fluidic flow to channel smaller than 1 mm in one or more dimension. since it involves a laminar flow of liquid, so it is a useful platform for fabricating low-cost sensing and detecting devices. Microfluidics is an important platform for Lab On Chip (LOC),where one or more operation can be operated on a single chip. There are diverse aspects to use microfluidic devices such as smaller sample volume and reagent consumption, shorten the time of experiments, controlled mixing and integrated multiple assays.It also reduces the costs of applications because of miniaturization. Research in paper-based sensing devices has been primarily increasing in recent years.The paper has historically been a primary choice because of its cellulosic structure and it can easily interact with the molecules due to its fibers nature. The unique properties of paper which allow it for sensing platform, it can easily transport the fluid via capillary action without any external source and compatibility with chemicals / biochemicals.It has also a high surface area to volume ratio[1]. Nowadays paper-based sensors are the alternative technology for fabricating analytical devices for many application areas including clinical diagnosis, food quality control, and environmental monitoring[2].Recent research is going to make the paper-based devices for biosensors, cell detection and point of care diagnostics.
The paper-based microfluidic devices can be fabricated by some of the standard techniques. We are describing some techniques, which are widely used. (a)Wax Patterning-Wax patterning technique can be divided by three different methods (i)Screen printing (ii)Wax dipping (iii)wax Printing (b)Photolithography-In this technique, we try to create a hydrophobic barrier using light onto the paper substrate. (c)Ink-jet printing-It is also an alternative technique which incorporates the paper sizing chemistry with digital inkjet printing technique to make paper-based devices[3]. All these techniques are widely used to make paper-based devices but there are also some of the drawbacks to using these techniques. The wax patterning technique has low resolution and not resistant to high temperature.The photolithography technique is very costly.It needs also complex steps, expensive reagents, and equipment.In other technique, we need to use an improved inkjet printer[3].
Poly-Di-Methyl-Siloxane(PDMS) is also a well-known substrate to make microfluidics devices because it has transparent property at a visible wavelength.It has also several benefits as ease of mass production and bond to glass or other PDMS layers through plasma treatment. Although there are some drawbacks to use PDMS as a substrate to make devices.It requires some external sources for fluidic flow but in the paper-based device, liquid flow is based on the capillary action it does not require any external force or sources for fluidic flow. PDMS has also a hydrophobic nature so that it can also absorb small hydrophobic molecules and there may be chances of swelling due to the presence of some small hydrocarbon solvent, water can also evaporate through it[4].Paper-based devices are easy to use, user-friendly and affordable.we can make disposable kind of system through paper.these are the several things to use paper-based rather than PDMS based.
The sensing devices use colorimetric and amperometric methods respectively for sensing.The colorimetric assay is widely used because the reagents are used and in the presence of analyte it produces the color change.this method is very easy to sense the presence of enzymes, specific compounds, antibodies, and analytes etc.Recently the first time chemotactic behavior have shown on a paper-based microfluidic device.Chemotaxis is the movement of biological species, in response to the influence of chemical stimulation[4].Sudake chaiyo et al. have seen the enzymatic detection of glucose on the disposable paper-based sensor using screen printed carbon electrode with phthalocyanineionic liquid graphene composite [5]. B. Manori Jayawardane et al. also developed recently the paper-based analytical device for water analysis.The water quality parameters can be analyzed such as the concentration of nutrients, heavy metals and organic contaminants, microorganism count and pH value [6].
Paper-based devices are the good platform for sensing approaches.In principle, it can have many application areas such as health diagnostics, environmental monitoring and food quality control[2].
Researchers are focusing on paper-based devices because of its easy fabrication techniques, simple operation and inexpensive.These devices can be non-invasive, very useful for point of care applications and disease diagnostic.
Materials Required
Nitro-Cellulose Membran(Whatman Protran BA 85,Sigma-Aldrich),Wax Paper, Digital Magnetic Spinot for heating (Tarsons,220V,50 Hz),ThermoMixer(eppendrof,1.5ml), Micropipette(2-20 μL),Battery (9 V,6F22 HIW),Microscope Glass Slides,Microtip,Baking Pad,Silver Conductive Paint,Multi meter.
Biomolecules
Antibody- Mouse Monoclonal Fatty Acid Binding Protein(FABP), Host-Mouse
Antigen- FABP Protein ,Source-Human Cardiac Tissue, Graphene Quantum Dots.
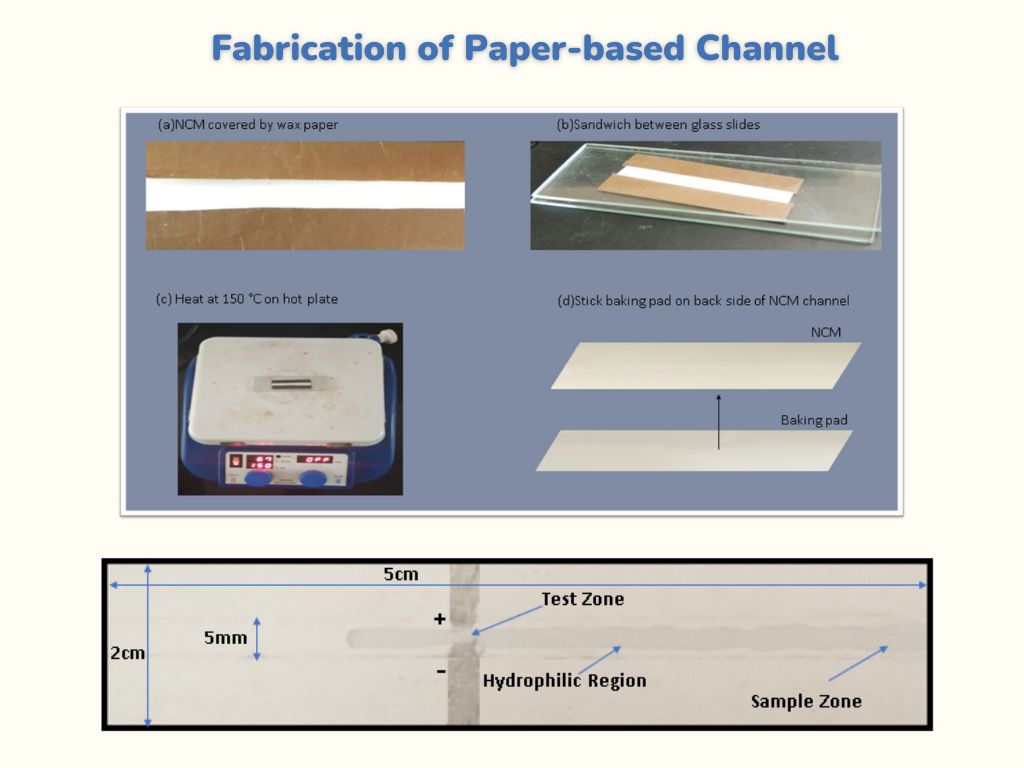
We use NCM(Nitro-Cellulose Membrane) and wax paper to make a paper-based microfluidic channel. The advantages to using NCM as a paper substrate because it is pure and has high surface area and excellent uniformity. This is also available in 0.2 μm and 0.45μm pore sizes and nitrocellulose varieties for peptide and protein applications, respectively. We first optimize the channel length and width on NCM, then we take a wax paper of the same length as channel length and sand-witch the NCM by wax paper except for channel region.
The use of wax paper is to make ahydrophobic barrier to fluidic flow through a hydrophilic channel. We fix this wax paper covered NCM channel into glass slides then heated on a magnetic heater at 150 ◦C for 120 seconds.Wax will melt on NCM and fill the pores of it and creates a hydrophobic barriers surrounding the hydrophilic channel.Hydrophobic region avoids the fluidic flow to cross its barrier because pores are filled with wax and fluid can flow in the hydrophilic region. Integration of electrodes with channel Screen printed electrode is made of silver conductive paint.Silver conductive paint is commercially available in the market.The channel region width is 5mm and the paper length and width is 2cm and 5cm respectively.We paste silver conductive paint on a channel and we give some gape between electrodes so fluid can flow and generate a resistive signal.Liquid flow is shown in the hydrophilic channel region from a Figure 2.2 .
We use NCM(Nitro-Cellulose Membrane) and wax paper to make a paper-based microfluidic channel. The advantages to using NCM as a paper substrate because it is pure and has high surface area and excellent uniformity. This is also available in 0.2 μm and 0.45μm pore sizes and nitrocellulose varieties for peptide and protein applications, respectively. We first optimize the channel length and width on NCM, then we take a wax paper of the same length as channel length and sand-witch the NCM by wax paper except for channel region.
The use of wax paper is to make ahydrophobic barrier to fluidic flow through a hydrophilic channel. We fix this wax paper covered NCM channel into glass slides then heated on a magnetic heater at 150 ◦C for 120 seconds.Wax will melt on NCM and fill the pores of it and creates a hydrophobic barriers surrounding the hydrophilic channel.Hydrophobic region avoids the fluidic flow to cross its barrier because pores are filled with wax and fluid can flow in the hydrophilic region. Integration of electrodes with channel Screen printed electrode is made of silver conductive paint.Silver conductive paint is commercially available in the market.The channel region width is 5mm and the paper length and width is 2cm and 5cm respectively.We paste silver conductive paint on a channel and we give some gape between electrodes so fluid can flow and generate a resistive signal.Liquid flow is shown in the hydrophilic channel region from a Figure 2.2 .
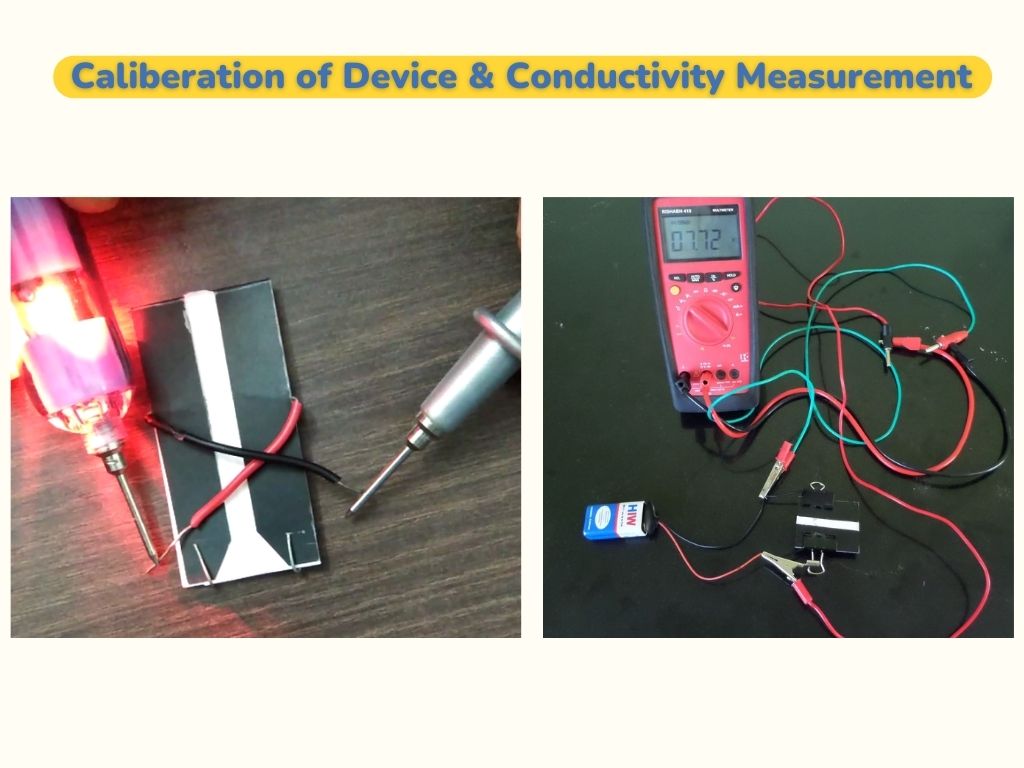
we can see the schematic diagram of device in Figure 2.3. Where channel is covered with the hard paper and only channel region can be seen. Battery is connected to Fig. 2.3. Schematic diagram of device electrode and resistance values is measured by multi-meter.
1. Conductivity Measurement
We first calibrated the device.We load the sample water liquid on sample zone of the channel, liquid flows through capillary action and when it reaches test zone, it Fig. 3.1. Calibration of device generates the electrical signal.
2. Resistance Measurement
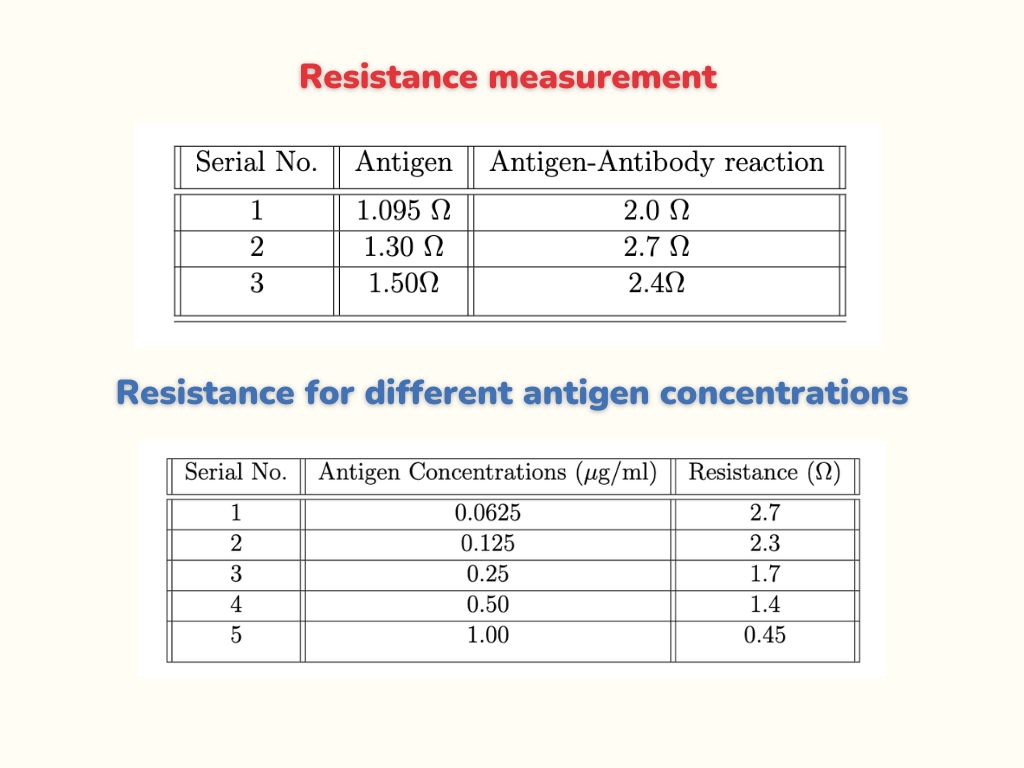
We first load the 5μL antigen on the sample zone using micropipette.When antigen passes from test zone,we measure resistance.Now, we bind the antibody on test zone, then we load the antigen ,when it passes from test zone, we again measure the resistance and found that the resistance of antibody-antigen reaction is greater than the resistance of antigen alone.The resistance values obtained are given in Table 3.1
We measured the resistance at different concentrations of antigen.First, we make the graphene-antibody conjugate solution by using a thermo-mixer and load 2μl on test zone.To bind it, we keep channel in an incubator for one hour. After binding, we took five different concentrations of antigen and five paper channels bind with graphene conjugated antibody.We load each antigen solution of different concentration on sample zone and when it passes from test zone, we get the resistance values that are shown in Table 3.2 .
We also plotted a graph of resistance values versus different concentrations of antigen.We found from Figure 3.2 that when concentration of antigen solution increases, resistance decreases.
We also plotted a graph of resistance values versus different concentrations of antigen.We found from Figure 3.2 that when concentration of antigen solution increases, resistance decreases.
We have designed and developed a paper based microfludic biosensor for detection of cardiac bio-marker ( H-FABP). It is very inexpensive and materials are easily available to make this device. This has a quicker fabrication technique and needs very low sample volume. The paper based microfluidic channel is created using Nitro-Cellulose Membrane and electrode is integrated with this channel using silver conductive paint.We measured the conductivity while fluid flow from test zone.We measured the Resistance of antibody-antigen reaction. We have seen that the resistance of antibody-Antigen reaction was greater than the resistance of antigen only.We also measured the antibody antigen reaction using different concentrations of antigen and plot a graph,it has shown that when value of concentration increases ,resistance decreases. It is found to be a very sensitive detection device which can be convert for long term non invasive diagnostic device.
[1] Yetisen, A. K., Akram, M. S., Lowe, C. R. (2013). Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab on a Chip, 13(12), 2210.
[2] Liana, D. D., Raguse, B., Gooding, J. J., Chow, E. (2012). Recent Advances in
Paper-Based Sensors. Sensors, 12(9), 11505-11526.
[3] He, Y., Wu, Y., Fu, J., Wu, W. (2015). Fabrication of paper-based microfluidic analysis devices: A review. RSC Advances, 5(95), 78109-78127
[4] Ilacas, G. C., Basa, A., Sen, A., Gomez, F. A. (2018). Enzyme Chemotaxis on Paper-based Devices. Analytical Sciences, 34(1), 115-119.
[5] Chaiyo, S., Mehmeti, E., Siangproh, W., Hoang, T. L., Nguyen, H. P., Chailapakul, O., Kalcher, K. (2018). Non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose with a disposable paper-based sensor using a cobalt phthalocyanineionic liquidgraphene composite. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 102, 113-120.
[6] Almeida, M. I., Jayawardane, B. M., Kolev, S. D., Mckelvie, I. D. (2018). Developments of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (PADs) for water analysis: A review. Talanta, 177, 176-190.
[7] Antibody and antigen. (n.d.). Retrieved April 05, 2018, from
http://www.scienceclarified.com/Al-As/Antibody-and-Antigen.html